Dataset upload¶
calcite upload¶
To upload a dataset to calcite, we recommand using our Command line interface.
Hint
npx @siliceum/calcite-cli [command arguments] let you run the command line directly.
Uploading with calcite-cli¶
Each project has a unique token, which is used when uploading a dataset. It can be found in the project details page, under the description of the project.
A dataset contains your datapoints and some metadata. It can either be provided in our json format or through a configuration file used to import the data.
Hint
A fake_bench.json file is provided as part of the example, and this is what we will use for our first upload.
Setup your CI so that the CALCITE_TOKEN environment variables contains your project token, and use the following command to upload the ./fake_bench.json dataset:
calcite upload ./fake_bench.json
Note
You can also specify more information via additional arguments:
- calcite upload [options] <filePath>
upload one dataset to a calcite server, by specifiying the config file, the gitRef and the commit id.
- -u, --url <server url>
Set the target server url, for preview and enterprise users. The CALCITE_URL environment variable can also be used, otherwise it will be set to the public server.
- -t, --token <token id>
Set the project token. By default the CALCITE_TOKEN environment variable is used.
- -C, --commit <sha>
Specify the full git commit sha.
- -R, --ref <gitref>
Specify the git ref.
- -BC, --benchconfig <sha>
Specify the benchmark config name.
- -BID, --buildId <id>
Specify the CI build number.
- -PR, --pullRequestId <id>
Specify the pull request number.
- --dry-run
Do not upload, instead print the content of the payload to the console.
- -h, --help
display help for command
Dataset formats¶
To understand why the data is organized the following way, please have a look at the Concepts documentation.
calcite JSon schema¶
calcite uses its own json schema to describe a dataset. Ultimately, this is what will be sent to the server, but you would usually create this file using an importer.
A lot of importers are being added, and will be open-sourced. Do not hesitate to contact us if you created a new one!
The schema is available here.
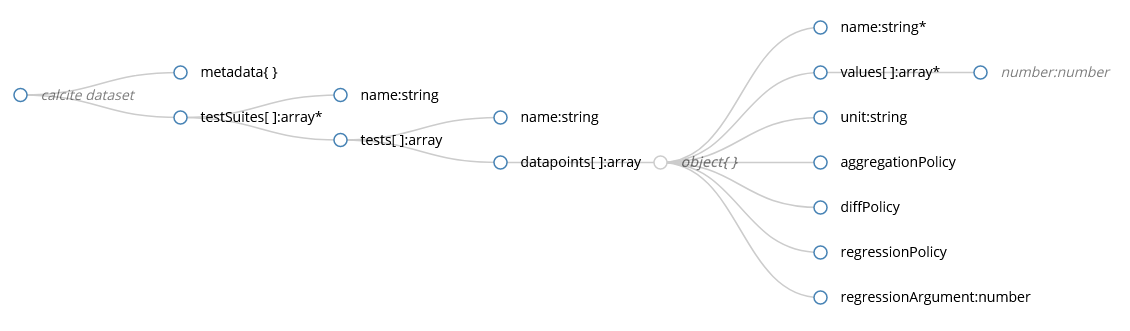
-
calcite dataset A benchmark dataset for use with calcite
-
metadata:object[optional]
-
testSuites:array - Items must be of type: #/definitions/TestSuite
-
-
definitions -
TestSuite A test suite regroups similar tests, or one test that was ran with different inputs.
-
name:string
-
tests:array - Items must be of type: #/definitions/Test
-
-
Test A test can report multiple datapoints, such as time, memory usage, etc. Tests using different input data are usually grouped in the same TestSuite
-
name:string
-
dataPoints:array - Items must be of type: #/definitions/Datapoint
-
-
Datapoint:object -
name:string
-
values:array The values that were sampled during the test.
-
unit:string The unit of this datapoint (s, ms, ns, Mb, Gb, MB, GB, W, …). This can be used to infer default values for other parameters of the datapoint.
-
aggregationPolicy This is the aggregation method used to summarize all values of a given commit and used for diffs between commits.
Values:- mean
- min
- max
- median
-
diffPolicy This describes how to compute the value used for regression detections.
substraction = target - baseline
relativeDifference = 100 * (target - baseline)/baseline (percentage)
none = ignore this datapoint
- substraction
- relativeDifference
- useTargetValue
- none
-
regressionPolicy Describes how fluctuations of values must be interpreted for regressions. absoluteDifferenceThreshold means that changes in any direction will be interpreted as regressions. equal means that any value different than regressionArgument will be treated as a regression.
Values:- lessIsBetter
- moreIsBetter
- absoluteDifferenceThreshold
- equal
-
regressionArgument:number[optional] This is the argument used in conjonction with the diff and regression policies. This could be an absolute value or percentage, based on the diff policy.
-
-
- Example
{ "testSuites": [ { "name": "someTestSuite", "tests": [ { "name": "someTestName", "dataPoints": [ { "displayName": "", "aggregationPolicy": "avg", "diffPolicy": "sub", "regressionPolicy": "lessIsBetter", "regressionArgument": 0, "name": "duration", "values": [0.11,0.128,0.091,0.089,0.102,0.098,0.102,0.101,0.099,0.107], "unit": "s" } ] } ] } ] }
Importing from other formats¶
Importing from other formats is best handled by specifying a .js file (usually calcite.config.js) instead of a .json file to the calcite upload command.
The cli expects the configuration file to export a function returning a calcite .json file.
This way you can write or reuse any kind of importer.
- Example
npx calcite upload ./calcite.config.js
calcite.config.js// Require modules, create functions, anything you want here... const getTestDatapoints = (testname) => { // ... } // Export the function to be called by the cli // It must return a valid calcite JSon object. module.exports = async () => ( testSuites: [ { name: 'fake testSuite', tests: [ { name: 'sometest', datapoints: getTestDatapoints('sometest') }, { name: 'othertest', datapoints: getTestDatapoints('othertest') }, ] }, ] });
Available importers¶
The following importers are available:
C++¶
Google benchmark (WIP)
nanobench (WIP, need to upstream)
Rust¶
Official microbenchmarking library (WIP)
Load testing¶
JMeter (WIP)
Gatling (WIP)
NeoLoad (WIP)
Web¶
Lighthouse CI (WIP)
Importer user example¶
@TODO@ How to use importers ? Via npm ? Copy the file directly ?